In a new study, scientists have uncovered a powerful new use for abnormal cannabinoid (AbnCBD) derivatives.
 These unique compounds, distinct from traditional cannabinoids, have shown remarkable effectiveness in combating drug-resistant Candida species, notes the study’s researchers. Published in Pharmacological Research, the study reveals how these derivatives not only inhibit fungal growth but also disrupt biofilm formation, offering a promising new approach to battling antifungal resistance.
These unique compounds, distinct from traditional cannabinoids, have shown remarkable effectiveness in combating drug-resistant Candida species, notes the study’s researchers. Published in Pharmacological Research, the study reveals how these derivatives not only inhibit fungal growth but also disrupt biofilm formation, offering a promising new approach to battling antifungal resistance.
The research was conducted by scientists from the University of Jerusalem, Ariel University, and The Hebrew University of Jerusalem. Their work focused on abnormal cannabinoids, a class of synthetic lipid compounds that, unlike traditional cannabinoids, do not interact with CB1 and CB2 receptors. Previous studies highlighted the cardioprotective and anti-inflammatory properties of one compound in particular, comp 3, as well as its antimicrobial potential against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).
Given the rise of antifungal drug resistance, particularly among Candida species, the researchers aimed to assess the antifungal capabilities of newly synthesized AbnCBD derivatives. The compounds were synthesized using acid catalysis-induced coupling, followed by further derivatization, to evaluate their impact on the growth of various Candida species.
Using in vitro colorimetric assays and in vivo mice experiments, the researchers demonstrated that AbnCBD derivatives induce differential inhibition of Candida growth. Compounds such as comp 3, comp 10, and comp 9 significantly reduced the growth of Candida albicans, including fluconazole (FLC)-resistant strains, as well as Candida tropicalis and Candida parapsilosis. However, Candida auris remained resistant to the treatment.
Comp 3 stood out among the compounds tested, as it not only inhibited the growth of C. albicans but also disrupted biofilm formation and eradicated mature biofilms—an important factor in overcoming persistent infections. While other derivatives disrupted biofilm formation, they did not affect yeast growth as effectively as comp 3.
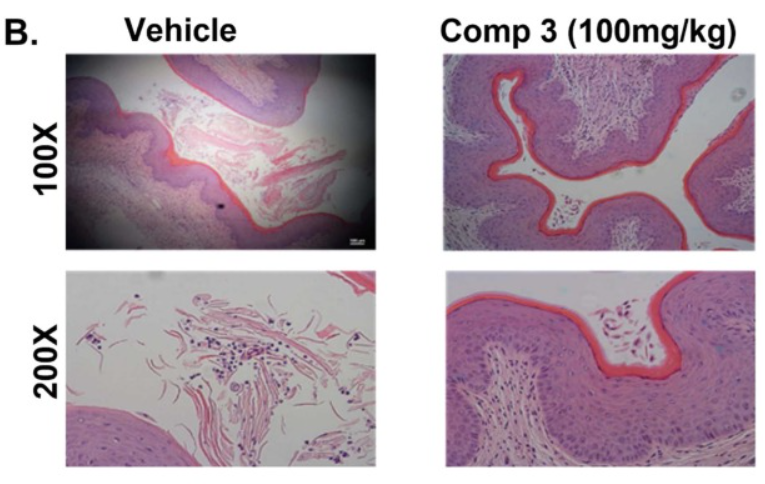
The effectiveness of comp 3 was further confirmed in a murine model of vulvovaginal candidiasis (VVC). In these tests, comp 3 demonstrated significant fungal clearance and reduced C. albicans burden compared to both vehicle and fluconazole controls.
“These findings highlight the potential of AbnCBDs as promising antifungal agents against Candida infections”, conclude the study’s researchers.
For more information on this study, click here.






