Researchers from South China Agricultural University have developed a novel hydrogel contact lens that releases cannabidiol (CBD) and citric acid in response to alkaline conditions, offering a promising new approach to treating corneal alkali burns (CAB). The research is presented in a new study published yesterday by the Journal of Controlled Release.

As noted by the study’s researchers, CABs are notoriously difficult to treat due to lingering alkali residues, bacterial infections, inflammation, and abnormal blood vessel growth. The healing process is highly sensitive to the local pH environment, which can remain disrupted following an alkali injury. The newly developed hydrogel lens addresses this by releasing citric acid to neutralize the alkaline microenvironment and CBD to reduce inflammation and oxidative damage.
The contact lens is made from a combination of citric acid-functionalized polyvinyl alcohol and quaternary ammonium chitosan, incorporating CBD through a freeze-thaw method that creates a strong interpenetrating polymer network. In tests, the hydrogel released over half of its citric acid and CBD payload within 24 hours when exposed to an alkaline environment.
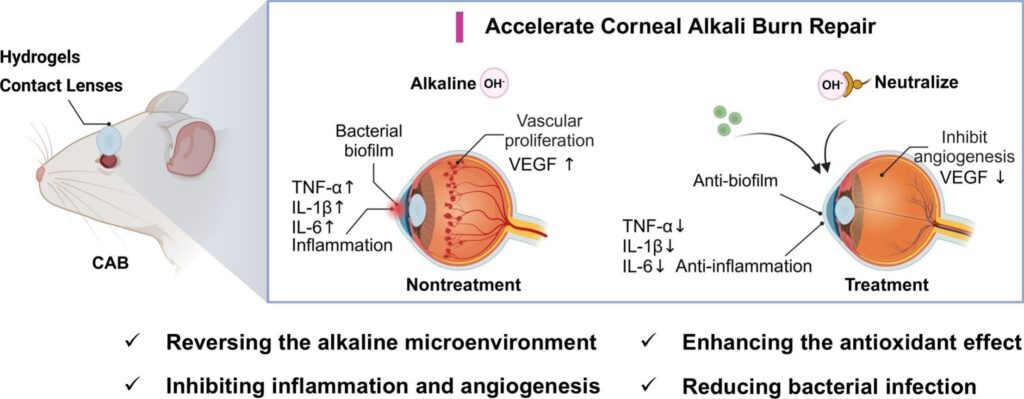
In addition to pH regulation, the lenses demonstrated strong antibacterial effects against E. coli and S. aureus, achieving over 90% inhibition by damaging bacterial membranes. The hydrogel was found to be highly biocompatible, with a hemolysis rate under 0.6% and cell viability over 90%. Animal testing confirmed the lenses helped reduce inflammation, inhibit unwanted angiogenesis, and promote healing in CAB cases.
The study’s authors conclude by saying “In conclusion, these results demonstrate the potential of this hydrogel CL for treating corneal alkaline burns, providing new insights into treatment of CAB.”
The full study can be found here.






