Cannabidiolic acid (CBDA) encapsulated in alginate microcapsules shows extended antioxidant activity and reduced cytotoxicity, according to a newly published study.
An image from the study.
The study, titled Alginate-based microencapsulation as a strategy to improve the therapeutic potential of cannabidiolic acid, explores an innovative method for enhancing the bioavailability and effectiveness of CBDA, a compound found in marijuana. The research, published in the International Journal of Pharmaceutics and epublished by the U.S. National Library of Medicine, also highlights CBDA’s potential as a natural therapeutic compound.
“Cannabidiolic Acid (CBDA) is a promising natural compound with potent antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-emetic properties”, states the study. “Its antioxidant activity rivals that of vitamin E, while its anti-inflammatory effects are also remarkable.”
Additionally, “CBDA has been shown to effectively reduce nausea and emetic attacks. As a more natural and water-soluble alternative to CBD, CBDA offers improved bioavailability and absorption. However, despite its promising potential, the development of effective CBDA delivery systems is still in its early stages.”
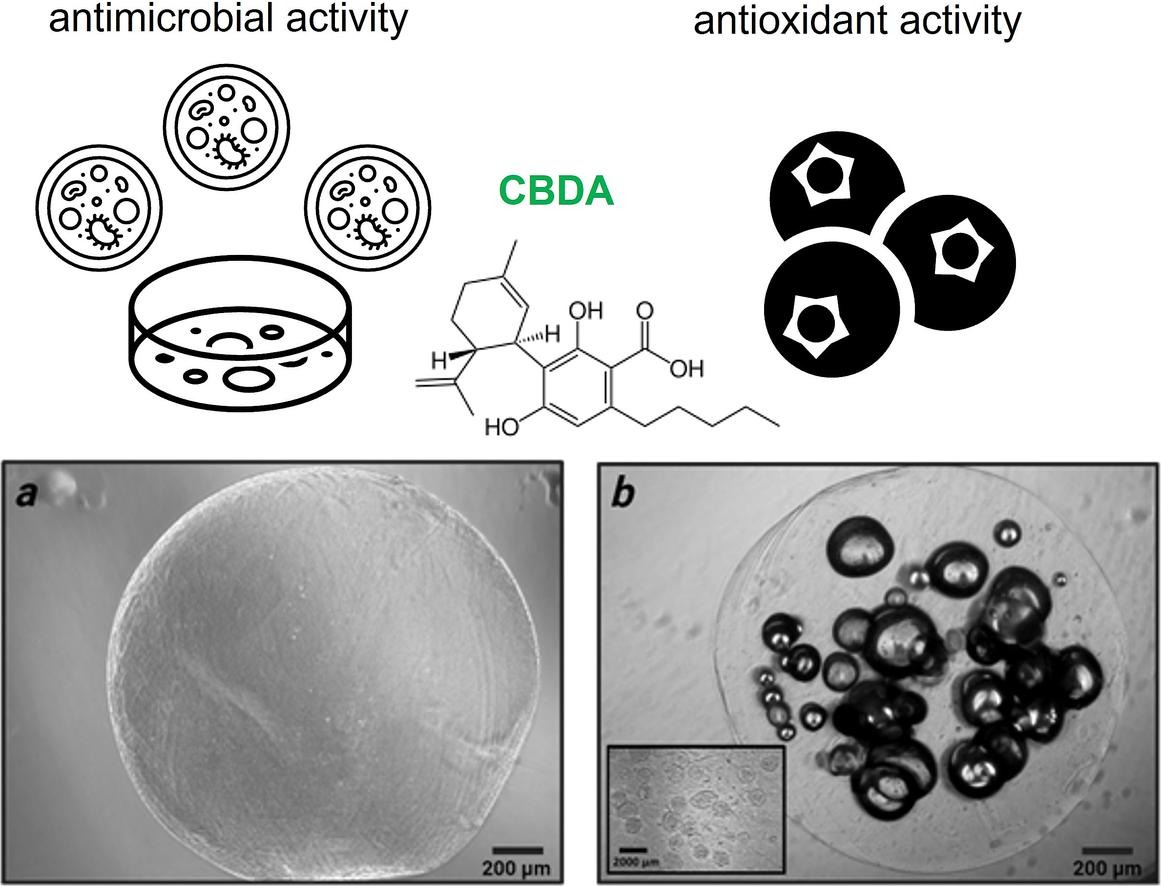
Researchers say that among the various materials suitable for drug delivery, “alginate is a widely used biopolymer due to its abundance and common availability in nature.” With that in mind, this study “aimed to develop an efficient CBDA delivery carrier using a microflow-dripping method to microencapsulate CBDA into alginate carriers (Alg-CBDA).”
The antioxidant, antimicrobial, and cytotoxicity properties of these Alg-CBDA capsules were evaluated by a team of reseachers.
“Our results demonstrated that encapsulating CBDA within alginate capsules yielded a novel multifunctional biomaterial with prolonged antioxidant activity up to 72 h and antimicrobial activity against Gram-positive bacteria. Furthermore, the encapsulation process significantly reduced CBDA’s cytotoxicity, broadening its potential applications.”
Researchers say that “To our knowledge, this is the first study demonstrating the advantages of CBDA within a drug delivery framework.”







