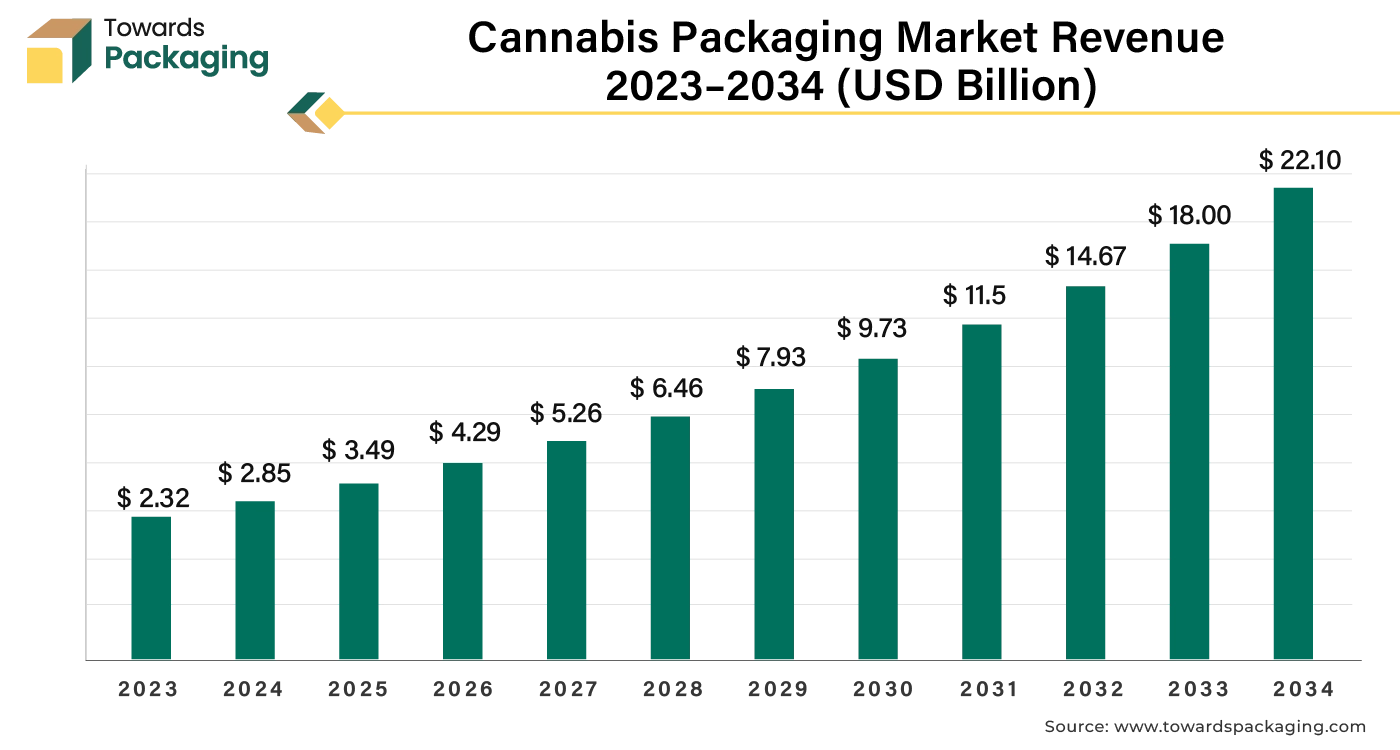
A recent literature review published in the journal Cells by explores the multifaceted therapeutic effects of cannabidiol (CBD) on the gastrointestinal (GI) system.
This non-psychotropic compound, found in Cannabis sativa, has demonstrated promising modulatory effects across various bodily systems, including the central nervous and immune systems.
The review, conducted by researchers from the University of Toledo, the University of Louisville School of Medicine, and Tulane University School of Medicine, highlights CBD’s ability to interact with multiple receptors—both cannabinoid and non-cannabinoid—while also exhibiting antioxidant properties that function independently of these receptors. These interactions play a crucial role in influencing intestinal permeability, the microbiome, immune cells, and cytokines, making CBD a potential therapeutic agent for conditions like inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Continue reading